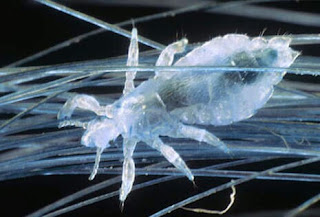
A sesame seed-size parasite that feeds on human blood, the head louse (Pediculus humanus capitis) is a nuisance known around the world. These tiny insects infest human hair and can also sometimes be found in the eyebrows and eyelashes.
Signs & symptoms
Some people with lice never realize they're infested. However, there are several telltale signs that the bugs are present on the scalp, according to the Mayo Clinic. These include:
- A ticklish feeling on the scalp or neck.
- An itchy scalp (the result of an allergic reaction to the bug's saliva).
- Small red bumps on the scalp, neck and shoulders.
- The presence of lice on the scalp.
- The presence of nits (lice eggs) on shafts of hair.
- Difficulty sleeping, which can lead to irritability. Some people with lice may also develop sores on their scalp. Such sores are likely the result of bacteria from the person's own body infecting an opening in the skin made by scratching, according to the CDC. Some people may scratch their scalps raw due to the itch and cause skin infections, said Margaret Khoury, a pediatric infectious disease specialist with Kaiser Permanente.
Diagnosis
The best way to confirm an active lice infestation is to find a live louse on the head, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP). Because lice move quickly and avoid light, it's best to check for them after wetting the hair, which some experts say slows the insects down.Treatment
There are several treatment options for those with head lice, including shampoos and creams that contain pediculicides,

Comments
Post a Comment